
Dr. Lutheran M. Carter IV
This portfolio was created to demonstrates my ability to describe and analyze learning theories. My portfolio includes descriptions, strengths, limitations, and implications of various learning theories in teaching and learning.
Comparing Learning Theories
Behaviorism
According to Vannack (2012), it is a school of thought that places significance on the role of experience in governing behavior in a way that initiates the behavior and includes specific behavior by the instructor that motivates the learner through interaction within the environment. To illustrate, behaviors within the classroom can be learned through conditioning and reinforcement such as rewards and punishments with is similar to the transactional leadership component of Bass and Avolio’s (2004) full-range leadership model (Mekonnen, 2004).
Strengths: Behaviorism can create a foundation of healthy and production organizations. For example, instructors can apply behavioral techniques to facilitate learning by enhancing learners’ understanding (Peel, 2005). Another pro is learning objectives during the instructional process (Ng’andu et al., 2013). Additionally, instructors can create a favorable environment for learners (Ng’andu et al., 2013).
Limitations: The entire process that occurs with the learners’ mind is not entirely considered, mainly concerning the stimuli and how learners respond (Strauch & Omar, 2014). However, role modeling, goal setting, and self-reinforcement can help learners achieve the required goals (Peel, 2005).
Implications: The goal of behaviorism-focused instructional design is eLearning must provide learners with appropriate stimuli. To illustrate, the instructional design must provide opportunities that assist learners in demonstrating that they can express the desired behaviors that prove that learning has occurred (Keramida, 2015).
References
Bass, B., & Avolio, B. (2004). Multifactor leadership questionnaire: Manual and sample set. (Technical Report). Redwood City, CA: Mind Garden Inc. https://www.mindgarden.com/multifactor-leadership-questionnaire/234-mlq-trainers-guide.html?search_query=multifactor&results=32
Keramida, M. (2015). Behaviorism in instructional design for eLearning: When and how to use it. eLearning Industry. https://elearningindustry.com/behaviorism-in-instructional-design-for-elearning-when-and-how-to-use
Mekonnen, W. (2020). Review on behaviorist approach and the construction of knowledgehttps://10.14662/IJELC2020.125
Ng’andu, K., Hambulo, F., Haambokoma, H., & Tomaida, K. (2013). The contribution of behaviourism theory to education. Zambia Journal of Education, 1(4), 58-74.
Peel, D. (2005). The significance of behavioural learning theory to the development of effective coaching practice. International Journal of Evidence Based Coaching and Mentoring, 3(1), 18-28. https://doaj.org/article/b7c99d948ee84c9e922e1f2628d15710
Vannack, H. (2012). The application of behaviourism in the classroom in primary and secondary schools. (). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/345397887_The_Application_of_Behaviourism_in_the_Classroom_in_Primary_and_Secondary_Schools
Strauch, C. C., Muaed, J., & Alomar. (2014). Critical analysis of learning theories and ideologies and their impact on learning evaluation of hospital admission criteria for community acquired-pneumonia patients at a private hospital in UAE view project
Cognitivism

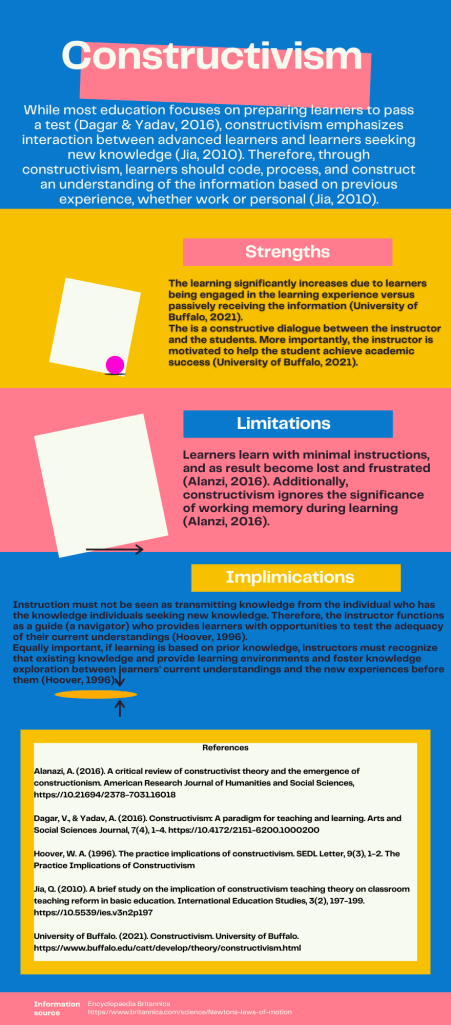
Constructivism
Andragogy
PERSONAL Experiences
Elementary School
Early 1990s
United States Navy
2012 – 2015
College
2009 – 2012
Behaviorism
Constructivism
Cognitivism OR
Connectivism
Andragogy
Authentic Assessment
MicroLearning
Project
Let’s make something together.